In social media channels, high quality content is the first priority, followed by content distribution. Companies worldwide invest large sums to create quality content, but in many cases, the content is not distributed properly. Audiences neither find nor share it. A good Content Creation and Distribution Plan for social media marketing will ensure that a company’s content is relevant, timely, and well written and that it reaches the target audience using the optimal means as determined by the digital marketing team.
One of the major debates regarding content creation is between content quality and quantity—how much content is enough and how good does it need to be?
Content creation should ideally start by defining a quantity goal and a publishing schedule with appropriate deadlines. Once the publishing schedule is finalized, focus should be on the quality for each piece of content being distributed.
Some of the different types of content that can be created for the various social media elements are as follows:
- Status updates—for professional and personal sharing websites
- Photos—for professional and personal sharing websites
- Videos—for audio-visual sharing, professional, and personal sharing websites
- Infographics—for blogs, discussion forums, and professional sharing websites
- Polls—for blogs, professional, and personal sharing websites
- Quizzes—for blogs, professional, and personal sharing websites
- Contests—for blogs, discussion forums, and professional sharing websites
It is also important to note that both the relevance of content and the relevance of type of content depend on the nature of the business. For example, quizzes are more relevant for companies in the education sector than for other industries such as manufacturing or airline.
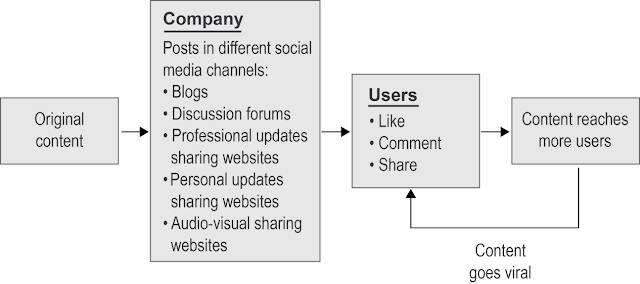
In addition to good quality content, an effective social media plan must have a good distribution strategy. The content should be shared through the company’s own blog as well as other company pages on various social media sharing sites. Businesses must also ensure that there are ways for their target audiences to like, comment, and share the original content created by the company.
The following figure shows a sample of the structure of a Content Creation and Distribution Plan.
To Know More,Please Visit - www.scrumstudy.com

